Recommended infrastructure on AWS
OpenNext does not create the underlying infrastructure. You can create the infrastructure for your app with your preferred tool — SST, AWS CDK, Terraform, Serverless Framework, etc.
This is the recommended setup.
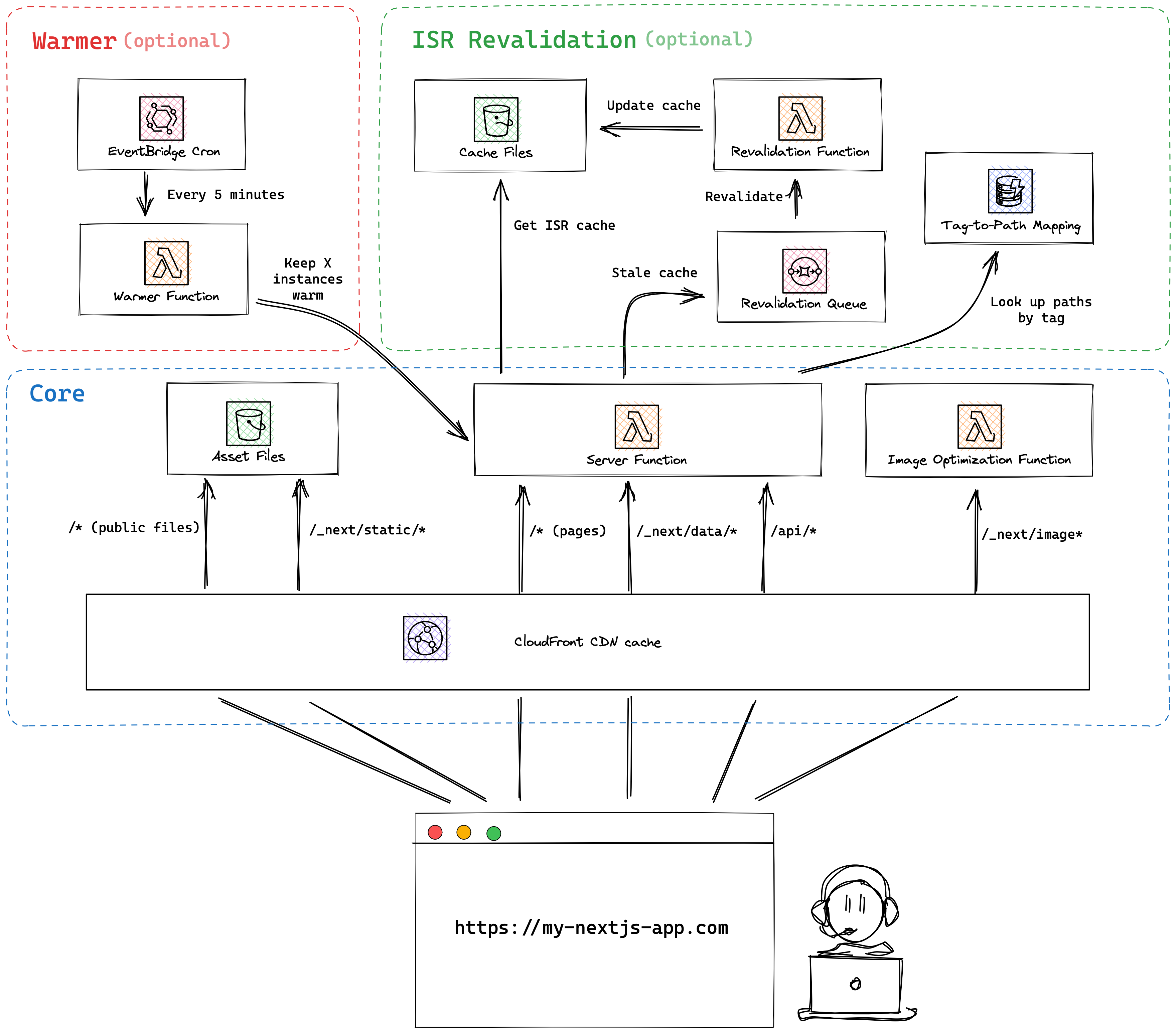
Here are the recommended configurations for each AWS resource.
Asset files
Create an S3 bucket and upload the content in the .open-next/assets folder to the root of the bucket. For example, the file .open-next/assets/favicon.ico should be uploaded to /favicon.ico at the root of the bucket. If you need to upload the files to a subfolder within the bucket, refer to this section.
There are two types of files in the .open-next/assets folder:
Hashed files
These are files with a hash component in the file name. Hashed files are be found in the .open-next/assets/_next folder, such as .open-next/assets/_next/static/css/0275f6d90e7ad339.css. The hash values in the filenames are guaranteed to change when the content of the files is modified. Therefore, hashed files should be cached both at the CDN level and at the browser level. When uploading the hashed files to S3, the recommended cache control setting is
public,max-age=31536000,immutableUn-hashed files
Other files inside the .open-next/assets folder are copied from your app's public/ folder, such as .open-next/assets/favicon.ico. The filename for un-hashed files may remain unchanged when the content is modified. Un-hashed files should be cached at the CDN level, but not at the browser level. When the content of un-hashed files is modified, the CDN cache should be invalidated on deploy. When uploading the un-hashed files to S3, the recommended cache control setting is
public,max-age=0,s-maxage=31536000,must-revalidateCache files
Create an S3 bucket and upload the content in the .open-next/cache folder to the root of the bucket. If you need to upload the files to a subfolder within the bucket, refer to this section.
There are two types of caches in the .open-next/cache folder:
- Route cache: This cache includes
htmlandjsonfiles that are prerendered during the build. They are used to seed the revalidation cache. - Fetch cache: This cache includes fetch call responses, which might contain sensitive information. Make sure these files are not publicly accessible.
Revalidation Table
Create a DynamoDB table with the following configuration:
- Partition key:
tag(String) - Sort key:
path(String) - An index named
revalidatewith the following configuration:- Partition key:
path(String) - Sort key:
revalidatedAt(Number)
- Partition key:
Image optimization function
Create a Lambda function using the code in the .open-next/image-optimization-function folder, with the handler index.mjs. Also, ensure that the function is configured as follows:
- Set the architecture to
arm64. - Set the
BUCKET_NAMEenvironment variable with the value being the name of the S3 bucket where the original images are stored. - Set the
BUCKET_KEY_PREFIXenvironment variable if the asset files are uploaded to a subfolder in the S3 bucket. The value is the path to the folder. This is Optional. - Grant
s3:GetObjectpermission.
This function handles image optimization requests when the Next.js <Image> component is used. The sharp (opens in a new tab) library, which is bundled with the function, is used to convert the image. The library is compiled against the arm64 architecture and is intended to run on AWS Lambda Arm/Graviton2 architecture. Learn about the better cost-performance offered by AWS Graviton2 processors. (opens in a new tab)
Note that the image optimization function responds with the Cache-Control header, so the image will be cached both at the CDN level and at the browser level.
Server Lambda function
Create a Lambda function using the code in the .open-next/server-function folder, with the handler index.mjs. Also, ensure that the function is configured as follows:
- Set the
CACHE_BUCKET_NAMEenvironment variable with the value being the name of the S3 bucket where the cache files are stored. - Set the
CACHE_BUCKET_KEY_PREFIXenvironment variable if the cache files are uploaded to a subfolder in the S3 bucket. The value is the path to the folder. This is optional. - Set the
CACHE_BUCKET_REGIONenvironment variable with the value being the region of the S3 bucket. - Set the
REVALIDATION_QUEUE_URLenvironment variable with the value being the URL of the revalidation queue. - Set the
REVALIDATION_QUEUE_REGIONenvironment variable with the value being the region of the revalidation queue. - Set the
CACHE_DYNAMO_TABLEenvironment variable with the value being the name of the revalidation table. - Grant
s3:GetObject,s3:PutObject, ands3:ListObjectspermission. - Grant
sqs:SendMessagepermission.
This function handles all other types of requests from the Next.js app, including Server-side Rendering (SSR) requests and API requests. OpenNext builds the Next.js app in standalone mode. The standalone mode generates a .next folder containing the NextServer class that handles requests and a node_modules folder with all the dependencies needed to run the NextServer. The structure looks like this:
.next/ -> NextServer
node_modules/ -> dependenciesThe server function adapter wraps around NextServer and exports a handler function that supports the Lambda request and response. The server-function bundle looks like this:
.next/ -> NextServer
+ .open-next/
node_modules/ -> dependencies
+ index.mjs -> server function adapterMonorepo
In the case of a monorepo, the build output looks slightly different. For example, if the app is located in packages/web, the build output looks like this:
packages/
web/
.next/ -> NextServer
node_modules/ -> dependencies from root node_modules (optional)
node_modules/ -> dependencies from package node_modulesIn this case, the server function adapter needs to be created inside packages/web next to .next/. This is to ensure that the adapter can import dependencies from both node_modules folders. It is not a good practice to have the Lambda configuration coupled with the project structure, so instead of setting the Lambda handler to packages/web/index.mjs, we will add a wrapper index.mjs at the server-function bundle root that re-exports the adapter. The resulting structure looks like this:
packages/
web/
.next/ -> NextServer
+ .open-next/
node_modules/ -> dependencies from root node_modules (optional)
+ index.mjs -> server function adapter
node_modules/ -> dependencies from package node_modules
+ index.mjs -> adapter wrapperThis ensures that the Lambda handler remains at index.mjs.
CloudFront distribution
Create a CloudFront distribution, and dispatch requests to their corresponding handlers (behaviors). The following behaviors are configured:
| Behavior | Requests | CloudFront Function | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
/_next/static/* | Hashed static files | - | S3 bucket |
/favicon.ico/my-images/*see why | public assets | - | S3 bucket |
/_next/image | Image optimization | - | image optimization function |
/_next/data/* | data requests | set x-forwarded-hostsee why | server function |
/api/* | API | set x-forwarded-hostsee why | server function |
/* | catch all | set x-forwarded-hostsee why | server function |
Running at edge
The server function can also run at edge locations by configuring it as Lambda@Edge on Origin Request. The server function can accept both regional request events (API payload version 2.0) and edge request events (CloudFront Origin Request payload). Depending on the shape of the Lambda event object, the function will process the request accordingly.
To configure the CloudFront distribution:
| Behavior | Requests | CloudFront Function | Lambda@Edge | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
/_next/static/* | Hashed static files | - | - | S3 bucket |
/favicon.ico/my-images/*see why | public assets | - | - | S3 bucket |
/_next/image | Image optimization | - | - | image optimization function |
/_next/data/* | data requests | set x-forwarded-hostsee why | server function | - |
/api/* | API | set x-forwarded-hostsee why | server function | - |
/* | catch all | set x-forwarded-hostsee why | server function | - |
Revalidation function
Create a Lambda function using the code in the .open-next/revalidation-function folder, with the handler index.mjs.
Also, create an SQS FIFO queue, and set it as the event source for this function.
This function polls the queue for revalidation messages. Upon receiving a message, the function sends a HEAD request to the specified route for its revalidation.
Warmer function
Create a Lambda function using the code in the .open-next/warmer-function folder, with the handler index.mjs. Ensure the function is configured as follows:
- Set the
FUNCTION_NAMEenvironment variable with the value being the name of the server Lambda function. - Set the
CONCURRENCYenvironment variable with the value being the number of server functions to warm. - Grant
lambda:InvokeFunctionpermission to allow the warmer to invoke the server function.
Also, create an EventBridge scheduled rule to invoke the warmer function every 5 minutes.
Read more on how warming works.
Dynamo Provider Function
This function is used to populate the revalidation table. It is a custom resource handler from the cdk see here (opens in a new tab). Ensure the function is configured as follows:
- Set the
CACHE_DYNAMO_TABLEenvironment variable with the value being the name of the DynamoDB table where the revalidation table is stored. - Grant
dynamodb:PutItempermission to allow the function to write to the DynamoDB table.